is_easy_mainland.png
%IM7DEV%magick ^ is_easy_mainland.png ^ -negate ^ -virtual-pixel Black ^ -distort depolar "-1,0,64,80" ^ -threshold 50%% ^ -process onewhite ^ nc_ex1.png
onewhite: 87,27

From a given coordinate, we can find the nearest point in an arbitrary area.
If white pixels represent the sea and black pixels represent land, with an arbitrary boundary between them, and we have a point on the sea, we can find the nearest coastal point.
Scripts on this page assume that the version of ImageMagick in %IM7DEV% has been built with various process modules. See Process modules.
This method using polar distortion works, but the nearest white method shown below is generally better.
See Polar Distortions for a discussion of unrolling images around a defined central point (and rolling them back up).
The technique is to unroll the input image, with the given sea point as the central point. The image is negated to make the sea black and the land white. Then the highest white point on the unrolled image represents the nearest coastal point. From the found (x,y) coordinates of this white point on the unrolled image, we easily calculate (r,θ) for the distance r and angle theta from the central point in the input image and hence the (x',y') coordinates of the found point on the input image.
r = y * d/h
θ = x * 2.pi/w ... θ in radians
x' = x - r.sin(θ)
y' = y - r.cos(θ)
... where w and h are the image width and height, and d is the distance from the central point to the furthest corner.
For example, suppose we have is_easy_mainland.png from the Islands page, and want to find the nearest coastal point to the coordinate 64,80.
|
is_easy_mainland.png |

|
%IM7DEV%magick ^ is_easy_mainland.png ^ -negate ^ -virtual-pixel Black ^ -distort depolar "-1,0,64,80" ^ -threshold 50%% ^ -process onewhite ^ nc_ex1.png onewhite: 87,27 |

|
The command gives (x,y) in unrolled space. From this, (r,θ) and (x',y') can be calculated.
As x and y are integers, the precision of the calculated (x',y') coordinates is limited, and is improved by supersampling.
The script nearCoast.bat does this, calculating ncRAD, ncTHETA, ncCST_X and ncCST_Y. If an output filename is supplied, the script also makes a debugging image showing a circle centred on the given white point and passing through the coastal point, and a line between the two points.
The given coordinates can be specified as pixels, or as a percentage of the image width and height.
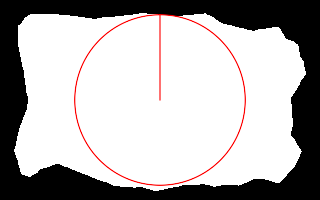
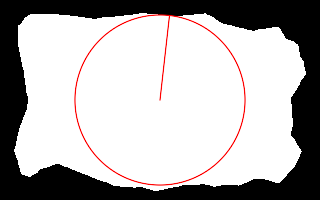
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ is_easy_mainland.png . . . nc_nc1.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=85.2159 ncTHETA=0 ncCST_CX=159.5 ncCST_CY=99.5 ncCST_X=159.5 ncCST_Y=14.2841 |
|
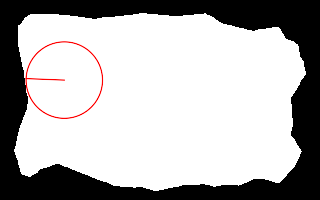
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ is_easy_mainland.png 20%%%% 40%%%% . nc_nc2.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=38.2159 ncTHETA=1.53153 ncCST_CX=63.8 ncCST_CY=79.6 ncCST_X=25.6136 ncCST_Y=78.0998 |
|
|
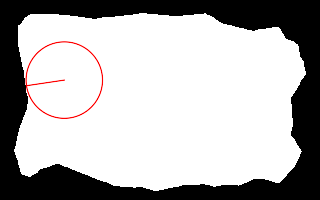
Repeat the previous, with more precision. set ncSUP_SAMP=4 call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ is_easy_mainland.png 20%%%% 40%%%% . nc_nc3.png set ncSUP_SAMP= echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=38.2159 ncTHETA=1.71806 ncCST_CX=63.8 ncCST_CY=79.6 ncCST_X=25.9977 ncCST_Y=85.2075 |
|
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ is_easy_mainland.png 60%%%% 70%%%% . nc_nc4.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=46.1613 ncTHETA=2.94524 ncCST_CX=191.4 ncCST_CY=139.3 ncCST_X=182.394 ncCST_Y=184.574 |
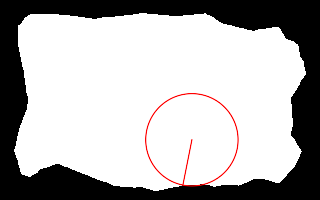
|
|
Repeat the previous, with more precision. set ncSUP_SAMP=4 call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ is_easy_mainland.png 60%%%% 70%%%% . nc_nc5.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% set ncSUP_SAMP= ncRAD=45.5695 ncTHETA=3.11214 ncCST_CX=191.4 ncCST_CY=139.3 ncCST_X=190.058 ncCST_Y=184.85 |
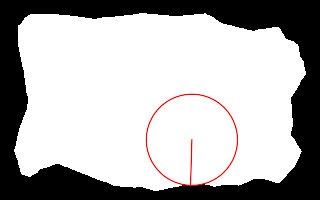
|
As the previous two examples show, increasing precision can have a significant impact.
The script is general-purpose: it will find the nearest black pixel to a given white coordinate, even if there are multiple clusters of black pixels.
|
Make a sample: %IMG7%magick ^ is_easy_mainland.png ^ -alpha off ^ -background Black -gravity Center -extent 200%%x200%% ^ -resize 25%% ^ -negate ^ ( +clone ) +append +repage ^ ( +clone ) -append +repage ^ nc_mult1.png |

|
|
Find the coastal point nearest to (40%,40%): call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_mult1.png 40%%%% 40%%%% . nc_m1.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=19.2922 ncTHETA=0.687223 ncCST_CX=127.6 ncCST_CY=79.6 ncCST_X=115.361 ncCST_Y=64.6869 |
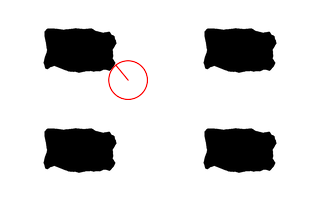
|
The sea doesn't need to be white. We might give a coordinate that is black.
|
Find the coastal point nearest to (21%,25%): call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_mult1.png 21%%%% 25%%%% . nc_blk1.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=0 ncTHETA=0 ncCST_CX=66.99 ncCST_CY=49.75 ncCST_X=66.99 ncCST_Y=49.75 ncRAD=0 means the given coordinate is not the sea. |

|
|
Declare the sea is black, and find the coastal point nearest to (21%,25%): set ncSEA_COL=black call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_mult1.png 21%%%% 25%%%% . nc_blk2.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncRAD=19.1269 ncTHETA=2.63108 ncCST_CX=66.99 ncCST_CY=49.75 ncCST_X=57.6441 ncCST_Y=66.4381 |
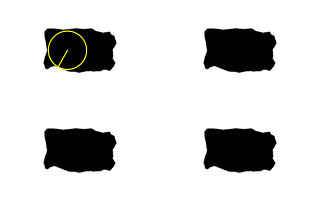
|
|
Automatically find the sea colour, and find the coastal point nearest to (21%,25%): set ncSEA_COL=auto call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_mult1.png 21%%%% 25%%%% . nc_blk3.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% set ncSEA_COL= ncRAD=0 ncTHETA=0 ncCST_CX=66.99 ncCST_CY=49.75 ncCST_X=66.99 ncCST_Y=49.75 |

|
If the sea is white, the script finds the nearest point that is less than 50% intensity. Similarly, when the sea is black, it finds the nearest point that is more than 50% intensity. The found point will be the "other" colour. When multiple points are to be found from random origins, flipping between two sides of a line can be avoided by ensuring the boundary is aliased, or by finding a thin edge between the black and white, and calling this the land.
|
Automatically find the sea colour, and find the coastal point nearest to (21%,25%): %IMG7%magick ^ nc_mult1.png ^ -edge 1 ^ -threshold 50%% ^ nc_edge1.png set ncSEA_COL=black call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_edge1.png 21%%%% 25%%%% . nc_e1.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% set ncSEA_COL= ncRAD=19.1269 ncTHETA=2.61145 ncCST_CX=66.99 ncCST_CY=49.75 ncCST_X=57.3184 ncCST_Y=66.2514 |
|
When the image is entirely sea, so there is no mainland:
%IMG7%magick ^ -size 100x100 xc:Black ^ nc_justsea.png call %PICTBAT%nearCoast ^ nc_edge1.png 21%%%% 25%%%% . nc_js_out.png echo ncRAD=%ncRAD% ncTHETA=%ncTHETA% echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% echo ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y%
ncRAD=0 ncTHETA=0 ncCST_CX=66.99 ncCST_CY=49.75 ncCST_X=66.99 ncCST_Y=49.75
Again, we have a return of ncRAD=0. In general, this should always be checked.
This technique can also be used to find corresponding coastal points. See Correlating shapes (not yet published).
The method shown above works. But unrolling the image takes time, the result is imprecise, and calculations are awkward.
As an alternative, we write a new process module, called nearestwhite that simply finds the nearest white pixel to the supplied coordinates.
The resulting script nearCoast2.bat is simpler and faster than nearCoast.bat. It doesn't offer supersampling because that would be of no benefit. It doesn't need to calculate RAD or THETA, so it doesn't. If there are no pixels of the required colour, nearCoast2.bat returns with ncCST_CX=-1.
nearCoast2.bat will always be quicker and more accurate than nearCoast.bat.
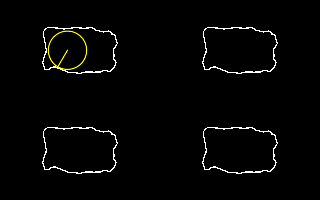
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast2 ^ is_easy_mainland.png . . . nc_nw_nc1.png echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% ^ ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncCST_CX=159.5 ncCST_CY=99.5 ncCST_X=169 ncCST_Y=15 |
|
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast2 ^ is_easy_mainland.png 20%%%% 40%%%% . nc_nw_nc2.png echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% ^ ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncCST_CX=63.8 ncCST_CY=79.6 ncCST_X=25 ncCST_Y=85 |
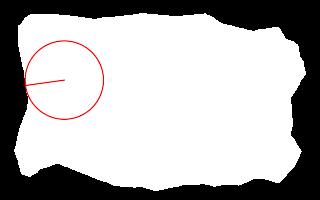
|
call %PICTBAT%nearCoast2 ^ is_easy_mainland.png 60%%%% 70%%%% . nc_nw_nc4.png echo ncCST_CX=%ncCST_CX% ncCST_CY=%ncCST_CY% ^ ncCST_X=%ncCST_X% ncCST_Y=%ncCST_Y% ncCST_CX=191.4 ncCST_CY=139.3 ncCST_X=200 ncCST_Y=184 |
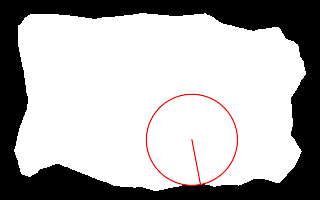
|
For convenience, .bat scripts are also available in a single zip file. See Zipped BAT files.
rem Given image %1 is black mainland around white "sea",
rem finds floating-point coordinates (ncX,ncY) of point on the mainland
rem nearest to given coordinate (%2,%3).
rem If the given coord is in the white "sea", the nearest point will be on the black "coast".
@rem
@rem %2, %3 coords of central point [default center of %1]
@rem Each coord may be suffixed with "%", for percentage of width or height.
@rem Default: centre of image.
@rem %4 proportion towards coast point (0 to 100) [100]
@rem %5 output debugging image [default NULL:, no output]
@rem
@rem Also uses:
@rem ncSUP_SAMP Factor for supersampling [default 1].
@rem ncPREFIX prefix for temporary files
@rem ncSEA_COL sea color: black, white or auto. Default white.
@rem auto will choose automatically, which takes time.
@rem nc?? automatic choice for negate
@rem nc?? if 1, assumes %1 is already supersampled and unrolled.
@rem
@rem Returns data about nearest point:
@rem ncRAD distance from given coord. 0 means given coord wasn't sea.
@rem ncTHETA bearing from given coord to found point, anti-clockwise from north.
@rem ncCST_X } x,y coord of found point.
@rem ncCST_Y }
@rem
@rem Updated:
@rem 16-July-2016
@rem 24-August-2022 for IM v7.
@rem
@if "%1"=="" findstr /B "rem @rem" %~f0 & exit /B 1
@setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
@call echoOffSave
call %PICTBAT%setInOut %1 nc
set CENT_X=%2
set CENT_Y=%3
if "%CENT_X%"=="." set CENT_X=
if "%CENT_Y%"=="." set CENT_Y=
set BLANK_CENT=0
if "%CENT_X%"=="" if "%CENT_Y%"=="" set BLANK_CENT=1
if "%CENT_X%"=="" set CENT_X=50%%
if "%CENT_Y%"=="" set CENT_Y=50%%
set X_SUFFIX=%CENT_X:~-1%
if "%X_SUFFIX%"=="%%" (
set nX=%CENT_X:~0,-1%
set X_MULT=^(w-1^)/100
) else (
set nX=%CENT_X%
set X_MULT=1
)
set Y_SUFFIX=%CENT_Y:~-1%
if "%Y_SUFFIX%"=="%%" (
set nY=%CENT_Y:~0,-1%
set Y_MULT=^(h-1^)/100
) else (
set nY=%CENT_Y%
set Y_MULT=1
)
set PROP=%4
if "%PROP%"=="." set PROP=
if "%PROP%"=="" set PROP=100
set OUTFILE=%5
if "%OUTFILE%"=="." set OUTFILE=
if "%OUTFILE%"=="" set OUTFILE=NULL:
set SUP_SAMP=%ncSUP_SAMP%
if "%SUP_SAMP%"=="." set SUP_SAMP=
if "%SUP_SAMP%"=="" set SUP_SAMP=1
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "WW=%%w\nHH=%%h\nnX=%%[fx:%nX%*%X_MULT%]\nnY=%%[fx:%nY%*%Y_MULT%]"
%INFILE%`) do set %%L
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "W_SS=%%[fx:%WW%*%SUP_SAMP%]\nH_SS=%%[fx:%HH%*%SUP_SAMP%]\nnXS=%%[fx:%nX%*%SUP_SAMP%]\nnYS=%%[fx:%nY%*%SUP_SAMP%]"
xc:`) do set %%L
rem echo %0: WW=%WW% HH=%HH% W_SS=%W_SS% H_SS=%H_SS% nX=%nX% nY=%nY% nXS=%nXS% nYS=%nYS%
if %BLANK_CENT%==1 (
set sUNROLL=-distort depolar "-1,0"
) else (
set sUNROLL=-distort depolar "-1,0,%nXS%,%nYS%"
)
if %SUP_SAMP%==1 (
set sSUP_UP=
) else (
set sSUP_UP=-resize "%W_SS%x%H_SS%^^^!"
)
if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="" set ncSEA_COL=white
if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="white" (
set sNEG=-negate
) else if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="black" (
set sNEG=
) else if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="auto" (
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "doNEG=%%[fx:p{0,0}.intensity>0.5?1:0]" ^
%INFILE%`) do set %%L
if "!doNeg!"=="1" (
set sNEG=-negate
) else (
set sNEG=
)
) else (
echo %0: bad ncSEA_COL "%ncSEA_COL%"
exit /B 1
)
for /F "usebackq tokens=1-3 delims=:, " %%W in (`%IM7DEV%magick ^
%INFILE% ^
%sNEG% ^
%sSUP_UP% ^
-virtual-pixel Black ^
%sUNROLL% ^
-threshold 50%% ^
-process onewhite ^
NULL: 2^>^&1`) do (
set MAGIC=%%W
set X=%%X
set Y=%%Y
)
if not "%magic%"=="onewhite" exit /B 1
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "dx=%%[fx:%nXS%>%W_SS%/2?%nXS%:%W_SS%-%nXS%]\ndy=%%[fx:%nYS%>%H_SS%/2?%nYS%:%H_SS%-%nYS%]"
%INFILE%`) do set %%L
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "RAD=%%[fx:%Y%/%SUP_SAMP%*hypot(%dx%,%dy%)/%H_SS%]\nTHETA=%%[fx:%X%*2*pi/%W_SS%]"
xc:`) do set %%L
for /F "usebackq" %%L in (`%IMG7%magick identify ^
-format "CST_X=%%[fx:%nX%-%RAD%*sin(%THETA%)]\nCST_Y=%%[fx:%nY%-%RAD%*cos(%THETA%)]"
xc:`) do set %%L
rem echo %0: RAD=%RAD% THETA=%THETA% CST_X=%CST_X% CST_Y=%CST_Y%
if /I not "%OUTFILE%"=="NULL:" (
if "%sNEG%"=="" (
set DBG_COL=yellow
) else (
set DBG_COL=red
)
%IMG7%magick ^
%INFILE% ^
-fill None -stroke !DBG_COL! ^
-draw "line %nX%,%nY% %CST_X%,%CST_Y%" ^
-draw "circle %nX%,%nY% %CST_X%,%CST_Y%" ^
-alpha off ^
%OUTFILE%
)
call echoRestore
@endlocal & set ncOUTFILE=%OUTFILE%& set ncRAD=%RAD%& set ncTHETA=%THETA%& set ncCST_CX=%nX%& set ncCST_CY=%nY%& set ncCST_X=%CST_X%& set ncCST_Y=%CST_Y%
rem Given image %1 is black mainland around white "sea",
rem finds floating-point coordinates (ncX,ncY) of point on the mainland
rem nearest to given coordinate (%2,%3).
rem If there are no white pixels, exits with ncCST_CX=-1.
rem If the given coord is in the white "sea", the nearest point will be on the black "coast".
@rem
@rem %2, %3 coords of central point [default center of %1]
@rem Each coord may be suffixed with "%", for percentage of width or height.
@rem Default: centre of image.
@rem %4 proportion towards coast point (0 to 100) [100]
@rem %5 output debugging image [default NULL:, no output]
@rem
@rem Also uses:
@rem ncPREFIX prefix for temporary files
@rem ncSEA_COL sea color: black, white or auto. Default white.
@rem auto will choose automatically, which takes time.
@rem nc?? automatic choice for negate
@rem nc?? if 1, assumes %1 is already supersampled and unrolled.
@rem
@rem Returns data about nearest point:
@rem ncCST_X x coord of found point, or -1 if none.
@rem ncCST_Y y coord of found point.
@rem
@rem Updated:
@rem 24-August-2022 for IM v7.
@rem
@if "%1"=="" findstr /B "rem @rem" %~f0 & exit /B 1
@setlocal enabledelayedexpansion
@call echoOffSave
call %PICTBAT%setInOut %1 nc2
set CENT_X=%2
set CENT_Y=%3
if "%CENT_X%"=="." set CENT_X=
if "%CENT_Y%"=="." set CENT_Y=
if "%CENT_X%"=="" set CENT_X=50%%
if "%CENT_Y%"=="" set CENT_Y=50%%
set PROP=%4
if "%PROP%"=="." set PROP=
if "%PROP%"=="" set PROP=100
set OUTFILE=%5
if "%OUTFILE%"=="." set OUTFILE=
if "%OUTFILE%"=="" set OUTFILE=NULL:
if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="" set ncSEA_COL=white
if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="white" (
set sNEG=-negate
) else if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="black" (
set sNEG=
) else if "%ncSEA_COL%"=="auto" (
echo %0: Error: 'auto' not available.
exit /B 1
) else (
echo %0: bad ncSEA_COL "%ncSEA_COL%"
exit /B 1
)
set X=
set CX=
for /F "usebackq tokens=1-3 delims=,= " %%W in (`%IM7DEV%magick ^
%INFILE% ^
%sNEG% ^
-virtual-pixel Black ^
-threshold 50%% ^
-process 'nearestwhite cx %CENT_X% cy %CENT_Y% v' ^
NULL: 2^>^&1`) do (
set MAGIC=%%W
if "!MAGIC!"=="nearestwhite.cx" (
set CX=%%X
) else if "!MAGIC!"=="nearestwhite.cy" (
set CY=%%X
) else if "!MAGIC!"=="nearestwhite:" (
set X=%%X
set Y=%%Y
)
)
if "%X%"=="" exit /B 1
if "%CX%"=="" exit /B 1
if "%X%"=="none" (
set X=-1
goto end
)
echo %0: CX=%CX% CY=%CY% X=%X% Y=%Y%
if /I not "%OUTFILE%"=="NULL:" (
if "%sNEG%"=="" (
set DBG_COL=yellow
) else (
set DBG_COL=red
)
%IMG7%magick ^
%INFILE% ^
-fill None -stroke !DBG_COL! ^
-draw "line %CX%,%CY% %X%,%Y%" ^
-draw "circle %CX%,%CY% %X%,%Y%" ^
-alpha off ^
%OUTFILE%
)
:end
call echoRestore
@endlocal & set ncOUTFILE=%OUTFILE%& set ncCST_CX=%CX%& set ncCST_CY=%CY%& set ncCST_X=%X%& set ncCST_Y=%Y%
All images on this page were created by the commands shown, using:
%IMG7%magick -version
Version: ImageMagick 7.1.0-42 Q16-HDRI x64 396d87c:20220709 https://imagemagick.org Copyright: (C) 1999 ImageMagick Studio LLC License: https://imagemagick.org/script/license.php Features: Cipher DPC HDRI OpenCL Delegates (built-in): bzlib cairo freetype gslib heic jng jp2 jpeg jxl lcms lqr lzma openexr pangocairo png ps raqm raw rsvg tiff webp xml zip zlib Compiler: Visual Studio 2022 (193231332)
%IM7DEV%magick -version
Version: ImageMagick 7.1.0-20 Q32-HDRI x86_64 2021-12-29 https://imagemagick.org Copyright: (C) 1999-2021 ImageMagick Studio LLC License: https://imagemagick.org/script/license.php Features: Cipher DPC HDRI Modules OpenMP(4.5) Delegates (built-in): bzlib cairo fontconfig fpx freetype jbig jng jpeg lcms ltdl lzma pangocairo png raqm rsvg tiff webp wmf x xml zip zlib Compiler: gcc (11.2)
To improve internet download speeds, some images may have been automatically converted (by ImageMagick, of course) from PNG or TIFF or MIFF to JPG.
Source file for this web page is nearcoast.h1. To re-create this web page, run "procH1 nearcoast".
This page, including the images, is my copyright. Anyone is permitted to use or adapt any of the code, scripts or images for any purpose, including commercial use.
Anyone is permitted to re-publish this page, but only for non-commercial use.
Anyone is permitted to link to this page, including for commercial use.
Page version v1.0 15-August-2015.
Page created 24-Aug-2022 21:10:26.
Copyright © 2022 Alan Gibson.